CCNA 3 Module 4 Exam Answers Version 3.1 1 Which statements are true concerning the shared memory buffering used by an Ethernet switch? (Choose two.) 2 What are the functions of routers? (Choose three.) 3 What are the functions of a Layer 2 Ethernet switch? (Choose three.) 4 Why does a switch have higher throughput compared to a bridge? 5 Why would a network administrator segment a network with a Layer 2 switch? (Choose two.) 6 7 Hubs are concerned with which PDU? 8 Which statements are true regarding hubs? (Choose three.) 9 Which device provides segmentation within a single network? 10 Which of the following is a Layer 2 broadcast address? 11 12 Which switching mode changes to store-and-forward mode after it detects a given number of errors? 13 Which form of buffering is used by bridges? 14 Where are switching tables stored in a Cisco LAN switch? 15 Which of the following are true regarding the addition of switches to a network? (Choose two.) 16 Which of the following is used to build a switching table? 17 Which statements describe asymmetric switching? (Choose three.) 18 What does switch latency describe? 19 How does an Ethernet bridge handle an incoming frame? (Choose three.) 20 Which attribute is used by a bridge to make forwarding decisions?
• Frames are processed through a single queue.
• All frames are placed in a common memory buffer.
• Frames are placed in a queue for the destination port.
• A port with a full memory buffer can cause frames for available ports to be delayed.
• Each switch port is statically assigned a buffer of equal size.
• improving network performance by increasing latency by twenty to thirty percent
• segmenting broadcast domains
• forwarding packets based on destination network layer addresses
• segmenting collision domains
• forwarding packets as soon as the destination MAC address is read
• developing routing table entries based on source IP addresses
• preventing broadcasts
• increasing available bandwidth per user
• decreasing the size of collision domains
• isolating traffic among segments
• routing traffic between different networks
• decreasing the number of broadcast domains
• Switching occurs in software.
• Switching occurs in hardware.
• Switches create multiple broadcast domains.
• Switches segment LANs.
• to create fewer collision domains
• to enhance user bandwidth
• to create more broadcast domains
• to eliminate virtual circuits
• to isolate traffic between segments
• to isolate ARP request messages from the rest of the network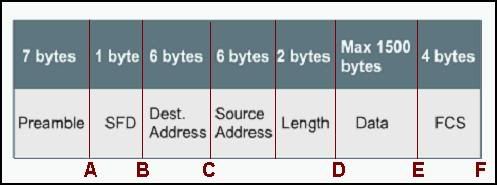
Refer to the graphic. Which point must be reached before a frame is forwarded when the switch is using store-and-forward mode?
• A
• B
• C
• D
• E
• F
• bits
• frames
• packets
• datagrams
• Hubs operate at Layer 1 of the OSI model.
• They create separate collision domains.
• Signals are distributed through all ports.
• Layer 2 addresses are used to make decisions.
• They calculate the CRC for each frame received prior to forwarding.
• Bandwidth is shared among all connected users.
• hub
• server
• switch
• transceiver
• 0.0.0.0
• 255.255.255.255
• 11:11:11:11
• FF:FF:FF:FF
• FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF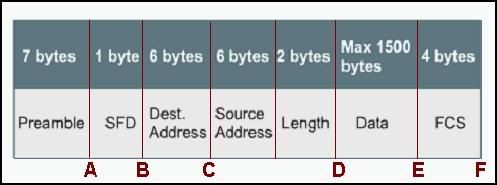
Refer to the graphic. Which point in the frame must be reached before it is forwarded by a switch that is using fast-forward mode?
• A
• B
• C
• D
• E
• F
• cut-through
• adaptive fast-forward
• fragment-free
• adaptive cut-through
• cut-through
• fragment-free
• fast-forward
• store-and-forward
• ROM
• CAM
• Flash
• SIMM
• NRAM
• They increase the number of collision domains.
• They decrease the number of collision domains.
• They increase the number of broadcast domains.
• They decrease the number of broadcast domains.
• They increase the amount of bandwidth available to users.
• They decrease the amount of bandwidth available to users.
• source IP addresses
• destination IP addresses
• destination MAC addresses
• source MAC addresses
• It uses data compression algorithms to manage higher bandwidth interfaces.
• It is often used to provide high bandwidth uplinks for a number of lower bandwidth client interfaces.
• It provides connections between network segments that operate at different bandwidths.
• It uses cut-through forwarding when going from a lower bandwidth to a higher bandwidth interface.
• It is used to provide more bandwidth to network clients than to backbone or server links.
• It may require buffering frames before forwarding to the destination interface.
• forwarding method used by a switch
• time it takes for a frame to be received by a switch
• improvement in network performance from using a switch
• time delay between when a frame enters and exits a switch
• increase in the size of a collision domain from using a switch
• The source MAC address and input interface pair are added to the bridging table.
• The destination MAC address and input interface pair are added to the bridging table.
• If no match to the destination MAC address is found in the bridging table, the frame is discarded.
• If no match to the destination MAC address is found in the bridging table, the frame is flooded out all other interfaces.
• If a match to the destination MAC address is found in the bridging table, the frame is forwarded out the associated interface.
• If a match to the source MAC address is found in the bridging table, the frame is forwarded to all ports.
• source IP address
• source MAC address
• destination IP address
• destination MAC address
• Layer 4-7 protocol address
Wednesday, 10 June 2009
CCNA 3 Module 4 Exam Answers Version 3.1
Labels: CCNA3-Version-3.1
Posted by 640-802-ccna at 6/10/2009 05:50:00 pm
Loading related posts...
CCNA3-Version-3.1
6/10/2009 05:50:00 pm
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)





0 comments:
Post a Comment